Skills Training for the Digital Economy: A Role-Based Approach
“The Fourth Industrial Revolution can be described as the advent of ‘cyber-physical systems’ involving entirely new capabilities for people and machines. While these capabilities are reliant on the technologies and infrastructure of the Third Industrial Revolution, the Fourth Industrial Revolution represents entirely new ways in which technology becomes embedded within societies and even our human bodies.”
To survive in today’s business landscape, companies must increase their use of digital technologies, transform their operations and processes, and reduce their dependence on in-person interactions. To thrive, business models and operations must be reimagined and rebuilt to take full advantage of 4IR technologies. In these times of stretching and growing, one thing is clear: the organisations that will thrive are the ones with the necessary talent to navigate the transition successfully. WEF “The Fourth Industrial Revolution can be described as the advent of ‘cyber-physical systems’ involving entirely new capabilities for people and machines. While these capabilities are reliant on the technologies and infrastructure of the Third Industrial Revolution, the Fourth Industrial Revolution represents entirely new ways in which technology becomes embedded within societies and even our human bodies.”
The digital transformation movement has caused companies worldwide and across industries to invest in intelligent systems and software to automate their processes and optimise their business models. However, what separates the digital transformation successes from the failures is access to talent that can apply new skills in relevant digital technologies successfully. Deviare takes a role-based approach. Here’s what this means: 1. Identifying the critical roles in an organisation to successfully deliver digital transformation goals throughout the different business areas. 2. Ensuring that each role has the right mix of skills to push the company’s digital transformation goals forward. 3. Creating an integrated learning path for each role, which delivers both digital skills and practical experience in application to business use-cases. This role-based approach contrasts with the skills-based approach taken by many learning libraries, where the focus is more on a large course collection and each course focusing on one skill. Developing the skills base of your organisation by choosing training courses from a catalogue as the need for that skill arises may seem a simple and effective approach, but this is a reactive method. It leaves you with crucial skill gaps while employees are being trained. Our comprehensive role-based approach to skills training was developed through a rigorous process: • Research and map industry trends. • Identify and list critical roles, and skills needed for each. • Develop learning paths that deliver these skills and the ability to apply them successfully
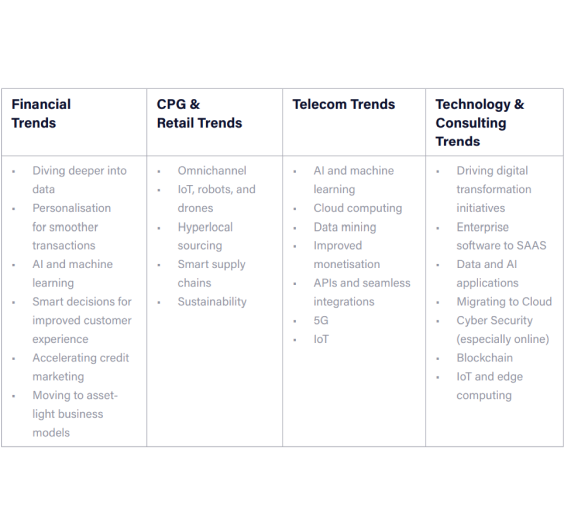
Research and map industry trends In order to develop a clear picture of the business models and operation transitions influencing industries, trends must be mapped out and understood. This provides clarity on the skills and roles needed to bring digital transformation to each. In the development of our role-based approach, four major global industries were mapped in detail: • Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI). • Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG) and Retail. • Telecommunications. • Technology and Consulting.
https://hubs.ly/Q02lW5QS0
https://hubs.ly/Q02lW5QS0
40% off
On all Data and AI Courses*
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur. Rhoncus placerat elementum hendrerit donec eu.
Button
Skills Training for Digital Economy: A Role-Based Approach
Case Study
Skills Training for the Digital Economy: A Role-Based Approach
Introduction We are today firmly within the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). Where steam drove the First Revolution, electricity drove the second, and digital computing drove the third, the Fourth Industrial Revolution is driven by interconnectivity and rapidly changing technologies. According to the World Economic Forum: “The technologies that define the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) include artificial intelligence, machine learning, robotics, data science, cloud computing, and the internet of things. In turn, these technologies have powered other new technologies like genetic engineering, which has transformed agriculture and medicine, and blockchain, which is transforming commerce.” Various pressures have compounded the pace of technological change, including the Covid-19 pandemic, which has changed how people socialise, work, and conduct business. These pressures have also accelerated 4IR’s pace – particularly here in Africa, where new and emergent technologies are driving rapid innovation across many sectors.

© 2024 Deviare
All rights reserved.
Solutions
Deviare Enterprise
Deviare Government
Deviare Learning Institution
Deviare Youth Campus
About Us
The Company
Our Team
Careers
Become A Partner
Affiliate Program
Resources
Whitepapers / Case Studies
Discussion Boards
Webinars
Career Development
Events
Success Stories/Testimonials
Radio Interviews
Blogs
Press Releases
Podcast
Community Forum
FAQs